What Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD)?
Posterior tibialis tendon dysfunction (PTTD) or Adult Acquired Flat Foot Deformity occurs when the posterior tibialis tendon no longer provides adequate support for the arch. This can result in arch collapsing and/or flattening of the foot. PTTD is a progressive condition which can continue to deteriorate if treatment is delayed.
What are symptoms of PTTD?
- Pain or swelling along the medial arch and ankle: This is often the most noticeable symptom, particularly during physical activity.
- Medial arch flattening/collapse: This can occur slowly over time, as the condition progresses the foot posture changes.
- Reduced range of motion in foot and ankle: The foot can become stiff and difficult to walk on uneven surfaces.
- Weakness or instability: The foot and ankle may feel weak or stiff while walking or completing activities.
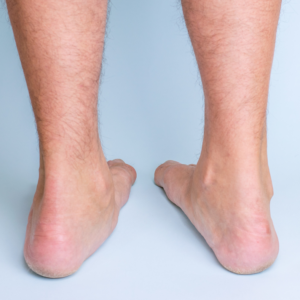
What Causes PTTD?
PTTD is caused by chronic inflammation of the posterior tibialis tendon. This progresses to degeneration and elongation of the tendon, with the formation of interstitial tears, and possible tendon rupture.
What Are the Treatment Options for PTTD?
- Orthotic devices or bracing: To give the arch the support it needs to reduce/manage symptoms with an ankle brace or a custom orthotic device which fits in shoes.
- Immobilisation: Immobilisation may be required in some cases with a CAM boot walker to allow the tendon to heal.
- Strengthening protocols: Exercise therapies may be prescribed to help rehabilitate the tendon and muscle.
- Shoe modification: Footwear assessment will be undertaken to determine appropriate footwear, recommendations can be made for adequate footwear. Bringing in your most worn footwear to your appointment is advised.
- Surgical Opinion: A surgical opinion may be recommended for further assessment and ongoing management if clinically indicated.
- Footwear: Footwear with adequate support and stability can be used as a tool in management of PTTD.
What are the stages of PTTD?
PTTD is a progressive condition that can be classified into four stages.
- Stage I: The tendon is injured but otherwise intact.
- Stage II: The tendon is torn (ruptured) or not working properly. The foot is deformed.
- Stage III: The foot is significantly deformed. There are degenerative changes to the connective tissue (cartilage) in the back of the foot.
- Stage IV: There are degenerative changes to the ankle joint.
How is Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD) Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of PTTD is usually made through a physical examination by a Podiatrist or Physiotherapist. Your clinician will assess your symptoms and may perform certain tests, such as:
- Resisted muscle testing: Trying to work the posterior tibialis tendon against increased resistance can reproduce symptoms.
- Palpation: Pressing on the medial calcaneal tuberosity and along the posterior tibialis tendon to check for pain or tenderness.
- Gait Analysis: Video gait analysis allows for assessment of the individual’s stance and walking pattern.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to assess the severity of the damage to the tendons. Especially if a tear is suspected.
When Should You See a Podiatrist?
If you’re experiencing persistent pain or discomfort around the medial arch or reduced arch height on both or one foot, it’s essential to seek professional help. We can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a tailored treatment plan to help you recover and prevent further injury.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction(PTTD) can be managed effectively with early intervention and the right care. If you’re concerned about ankle pain or would like more information, don’t hesitate to contact us or book online